ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles are reshaping the cotton industry. The focus is clear: reducing environmental impact, ensuring fair labor practices, and increasing supply chain transparency. Cotton farming uses 10% of global insecticides, faces water scarcity, and contributes significantly to CO2 emissions. However, initiatives like the U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol and the Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) are driving measurable improvements, such as reducing pesticide use, improving water efficiency, and enabling traceability.
Key takeaways:
- U.S. cotton growers have cut greenhouse gas emissions by 25% since 1980.
- BCI now covers 23% of global cotton production, with traceable cotton volumes rising sharply.
- Regenerative farming practices are reducing soil erosion and carbon emissions.
- Digital tools like QR codes and TraceBale ensure supply chain transparency.
Challenges remain, including water use, labor conditions, and Scope 3 emissions. Yet, frameworks like BCI v3.1 and technologies for environmental monitoring are helping producers and ginners meet stricter regulations and market demands. The future of cotton lies in balancing sustainability with profitability.
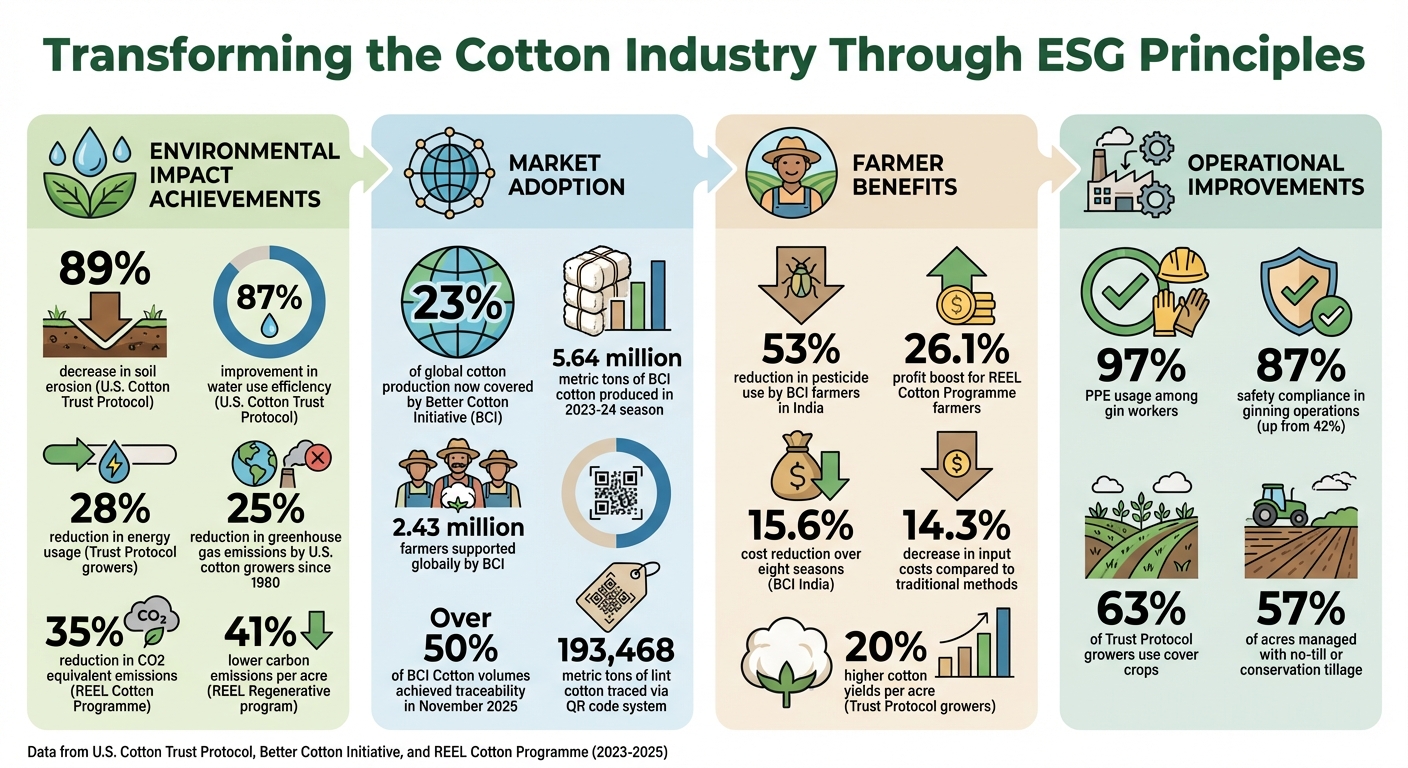
ESG Impact in Cotton Industry: Key Statistics and Achievements
Aus Cotton Conversations: Tackling the global challenges for cotton
sbb-itb-0e617ca
Current ESG Trends in the Cotton Sector
The cotton industry is tackling environmental, social, and governance (ESG) challenges head-on with focused strategies. Three key trends are driving this transformation: standardized certification programs, regenerative farming practices, and digital tools for transparency. These shifts are changing the way producers, ginners, and brands approach sustainability.
Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) Adoption
The Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) has evolved into a full certification scheme by 2025, significantly boosting accountability in sustainable cotton production. BCI now accounts for 23% of global cotton production, with 5.64 million metric tons produced in the 2023–24 season across 15 countries. Supporting around 2.43 million farmers globally, it stands as the largest sustainability program in the cotton sector.
In November 2025, over half of BCI Cotton volumes achieved traceability. This advancement allows brands to pinpoint the country of origin for "Physical BCI Cotton", moving away from credit-based systems. Between 2023 and late 2025, traceable volumes surged to over 23,000 metric tons, a sharp increase from just 90 metric tons in 2024. Brazil also accelerated its traceability goals, onboarding its cotton volumes into the BCI system by November 2025, two years ahead of its original 2027 target.
"The complexity of textile supply chains, combined with increased legislation, makes traceability non-negotiable." - Jacky Broomhead, Director of Traceability, Better Cotton Initiative
BCI's impact extends beyond traceability. A 2024 India Impact Report revealed that BCI farmers reduced pesticide use by 53% and cut costs by 15.6% over eight seasons. This success is attributed to Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques, which replace synthetic chemicals with biological and cultural methods. The updated Principles and Criteria (v3.1), effective April 2025, mandate the phasing out of Highly Hazardous Pesticides (HHPs) and emphasize climate action and social impact. These advancements highlight the industry's broader shift toward regenerative practices.
Growth of Organic and Regenerative Cotton Practices
Regenerative agriculture is gaining momentum as it focuses on rebuilding soil health, boosting biodiversity, and improving water quality. This approach goes beyond minimizing harm, aiming instead to create positive environmental outcomes.
BCI's updated Principles and Criteria (P&C) v3.1, introduced in April 2025, incorporate regenerative methods under the "Natural Resources" principle. The revised standard requires 2.13 million licensed farmers to adopt practices that actively enhance soil and biodiversity. Climate action and gender equality are now treated as "Cross-Cutting Priorities", integrated into all farm management decisions.
Field data underscores the effectiveness of regenerative agriculture. CottonConnect's REEL Regenerative program reported 41% lower carbon emissions per acre compared to control farms, tracked through annual monitoring. Additionally, the broader REEL Cotton program achieved a 35% reduction in CO2 equivalent, supported by digital monitoring and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies.
"The soil itself indicates what it needs. We must meet the soil's needs." - Yogeshbhai, Farmer
Geographically, the industry is expanding its reach. BCI has launched initiatives in Spain and Côte d'Ivoire, with plans for new programs in Benin and Cameroon. These efforts aim to double BCI cotton production by 2030, transitioning sustainable and regenerative cotton from a niche product to a global standard.
Digital Tools for Supply Chain Transparency
Technology is addressing one of the cotton sector's biggest ESG challenges: proving the origin of cotton and how it was cultivated. Digital platforms now allow real-time tracking from farm to finished product, offering verified data for compliance and consumer trust.
CottonConnect's TraceBale software exemplifies this innovation. During the 2023-24 season, the company introduced a QR code system for seed cotton procurement in its REEL Cotton and REEL Regenerative programs. Farmers received unique QR codes scanned by ginner representatives, enabling CottonConnect to trace 193,468 metric tons of lint cotton across regions like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Turkey.
"Last year we launched a new portal for our TraceBale system and supported the virtual chain of custody via improvements in the physical chain of custody, including unique QR codes for farmer purchases, and the roll-out of a DNA marker to provide further assurance from gin to garment." - Alison Ward, CEO, CottonConnect
The Better Cotton Platform also plays a crucial role, serving as a centralized hub for traceability. Launched at the end of 2023, it supports four Chain of Custody (CoC) models, including Segregation and Controlled Blending, to ensure traceable transactions. Over 2,000 supplier and manufacturer sites have adopted the CoC Standard to trade Physical BCI Cotton.
Digital tools are also enhancing environmental monitoring. The Cool Farm Tool tracks greenhouse gas emissions at both farm and program levels, while soil testing tools like Bhu-Parikshit provide on-site assessments of soil health. These innovations enable producers to make immediate adjustments and improve ESG reporting accuracy.
ESG Reporting Frameworks for Cotton Businesses
Today, cotton producers and ginners are expected to prove their sustainability efforts through standardized reporting. The right framework not only helps measure impact but also ensures compliance with regulations and builds trust with brands and consumers. Three key systems have become industry benchmarks: Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) Principles and Criteria v.3.1, REEL Cotton and Regenerative Standards, and Responsible Business for Gins (RB-Gins). These frameworks cover everything from farming practices to ginning operations.
Environmental Reporting Metrics
Environmental reporting begins by tracking essential indicators like water usage, chemical inputs, and yield performance. These Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the backbone of reliable ESG reporting.
Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) play a critical role in understanding environmental impacts across the cotton supply chain. The REEL Cotton Programme's 2024 LCA showed that sustainable practices can cut CO2 equivalent emissions by 35% per kilogram of fiber and reduce fossil fuel energy use by 36%. Key contributors to environmental impact include irrigation, fertilizer use, and emissions from fields.
In Gujarat, India, farmer Chandrakantbhai Vittalbhai Patel showcased how precise environmental monitoring can make a difference: shifting to drip irrigation reduced water consumption by 25-30% while boosting cotton yield by 30%.
The U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol has set benchmarks that highlight the potential of systematic monitoring. Since 2015, its members have achieved an 87% improvement in water use efficiency, a 25% drop in energy use, and an 89% decrease in soil erosion. These results underscore the value of committing to consistent environmental tracking and improvement.
"With new legislation and frameworks being implemented across key consumer markets, a focus on assuring the outcomes and impact of our work through strong monitoring and evaluation frameworks is essential." - Alison Ward, CEO, CottonConnect
While environmental metrics are crucial, social and governance reporting ensures that the human and operational aspects of cotton production are up to par.
Social and Governance Reporting Standards
In addition to environmental tracking, social and governance standards address labor practices and operational integrity. The BCI Principles and Criteria v.3.1, effective April 1, 2025, outline six core principles: Management, Natural Resources, Crop Protection, Fibre Quality, Decent Work, and Sustainable Livelihoods. Climate change and gender equality are treated as overarching priorities that must influence all farm-level decisions.
Decent work reporting focuses on key indicators like access to grievance mechanisms, fair wages, equal learning opportunities, and occupational safety risks. It also requires monitoring for child labor, forced labor, workplace harassment, and workers' freedom to organize. These social metrics have become essential as brands face growing pressure to ensure ethical supply chains.
The Responsible Business for Gins Code of Conduct tackles ESG challenges specific to ginning operations. For example, implementing Health, Safety, Security, and Environment (HSSE) protocols increased safety compliance from 42% to 87%, while Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) usage among gin workers rose to 97%. These changes highlight how governance standards can transform workplace conditions.
CottonConnect's Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD) Governance Framework helps businesses meet new corporate sustainability legislation. This framework is particularly relevant as regions like the European Union introduce mandatory supply chain transparency laws.
| Framework | Primary Focus | Key Principles | Cross-Cutting Priorities | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCI P&C v.3.1 | Field-level impact and improvement | Management, Natural Resources, Crop Protection, Fibre Quality, Decent Work, Sustainable Livelihoods | Climate Change Mitigation/Adaptation, Gender Equality | April 1, 2025 |
| REEL Cotton Standard | Data-driven insights, traceability | REEL Cotton Code, REEL Regenerative Code, Gin-specific conduct | Biodiversity, Waste Management, Soil Testing | REEL Regenerative 1.0 in May 2025 |
Tools for ESG Reporting and Compliance
Digital tools have revolutionized ESG reporting, turning what was once a tedious process into real-time tracking. For example, the TraceBale system records transactions across the cotton supply chain, from farmers to ginners and spinners. By enabling real-time tracking and verification, these tools ensure transparency.
The Cool Farm Tool specializes in greenhouse gas emissions tracking, helping producers calculate their annual carbon footprint with precision. For soil health, tools like Bhu-Parikshit provide on-site testing to monitor changes in organic matter and carbon levels. These technologies allow producers to move from rough estimates to verified, measurable outcomes.
Advanced systems like QR codes and DNA markers eliminate record-keeping errors and ensure traceability from the field to final reports. These innovations are critical as stricter regulations demand greater accountability.
The U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol offers a platform that provides field-level data and measurable outcomes for growers, mills, and retailers. This system allows participants to showcase responsible practices through verified data, replacing self-reported claims with concrete evidence.
Sustainability Strategies for Cotton Gins
Cotton gins play a key role in the supply chain, but their operations come with notable environmental challenges. Addressing these issues through ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) strategies is becoming increasingly important, aligning with broader efforts in sustainable cotton production. For example, CottonConnect has worked with over 100 gins in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh over six years, showing how targeted sustainability initiatives can transform operations. With tens of thousands of workers employed in this sector, it's crucial for brands to include ginning operations in their ESG goals.
Water and Energy Efficiency
The Responsible Business for Gins Code of Conduct offers a practical framework to evaluate and improve resource efficiency. Through Life Cycle Assessments, ginning operations can now measure their environmental footprint, identifying where water and energy consumption is highest. Training programs for gin owners, supervisors, and workers further support the adoption of HSSE (Health, Safety, Security, and Environment) best practices.
To meet tightening regulations around sustainability claims, independent verification of ginning processes is becoming standard. Tools like TraceBale provide digital traceability, delivering real-time data to help gins identify inefficiencies and make adjustments.
"A fully sustainable supply chain must include the ginning stage." - CottonConnect
Efforts to improve resource efficiency naturally extend to better waste management practices.
Waste Management and Circular Practices
Mechanical recycling offers a straightforward way for gins to repurpose cotton waste. By collecting, sorting, and shredding, waste fibers can be transformed into materials like thermal insulation, padding, or industrial wipes - all without chemical processing. For more advanced uses, chemical recycling breaks down cotton waste into pulp, enabling the creation of regenerated cellulose fibers with nearly 99% chemical recovery.
Recycled fibers and gin waste can also be used to strengthen biodegradable polymer composites, which find applications in automotive interiors, furniture, and building insulation. Additionally, producing mélange yarn from pre-colored waste fibers eliminates the need for traditional dyeing, significantly reducing water and chemical use. With 92 million tons of textiles discarded globally each year - and only 15% recycled - there's a massive opportunity for gins to tap into these waste streams.
The adoption of sorting technologies can further optimize recycling efforts by classifying waste based on fiber type and color. This reduces contamination and enhances the quality of recycled materials. Meanwhile, compliance with BCI (Better Cotton Initiative) Principles v.3.1 ensures the safe handling and storage of crop protection inputs, while phasing out the use of Highly Hazardous Pesticides.
Beyond internal improvements, collaboration across the sector can amplify sustainability efforts.
Using cottongins.org for ESG Networking
The cottongins.org directory connects cotton gins across the U.S., enabling them to locate BCI-compliant operations and exchange sustainability strategies. This platform also allows gins to showcase their ESG achievements, attract like-minded partners, and reinforce their commitment to ethical supply chain practices.
Gins can choose from three sponsorship plans to highlight their environmental initiatives:
| Sponsorship Plan | Monthly Cost | Primary Benefit | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sponsored Post | $200 per post | Highlight specific ESG updates or milestones; posts are featured for one day and shared on social media | Individual gins announcing certifications or technology upgrades |
| Official Sponsor | $200/month | Includes a logo and backlink on the main page footer, plus one free Sponsored Post with an annual commitment | Mid-sized gins seeking consistent ESG visibility |
| Featured Sponsor | $400/month | Offers top placement on the site and main page footer, along with two free Sponsored Posts annually | Large-scale operations driving sustainability across the sector |
Conclusion: ESG as a Competitive Advantage
In today’s global market, integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles isn't just a choice for cotton producers and ginners - it’s a necessity. With regulations like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) coming into effect, businesses without verifiable sustainability data risk losing access to crucial markets and premium partnerships. U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol growers, for example, have demonstrated impressive results: an 87% improvement in water use efficiency, an 89% reduction in soil loss, and 20% higher cotton yields per acre compared to the national average.
"With emerging regulations like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and growing stakeholder scrutiny, the need for verifiable, robust data has never been more important for brands and retailers." – Daren Abney, Executive Director, U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol
The demand for transparency is reshaping the industry. Brands now require traceable supply chains, and systems like TraceBale or the Trust Protocol platform offer cotton operations a clear edge when competing for contracts. This shift highlights ESG's dual role: ensuring compliance while driving growth opportunities.
The numbers tell the story. Trust Protocol growers have cut their energy usage by 28%, reducing costs and helping downstream partners meet Scope 3 emission targets. Similarly, farmers in the REEL Cotton Programme have experienced a 26.1% profit boost and a 14.3% decrease in input costs compared to traditional methods. These tangible results show how sustainability efforts can align with financial success, paving the way for broader industry resilience.
As the cotton sector contends with climate challenges, regulatory pressures, and rising stakeholder expectations, adopting regenerative farming practices, precision technologies, and recognized certifications is becoming essential. Today, 63% of Trust Protocol growers use cover crops, and 57% of acres are managed with no-till or conservation tillage practices. These methods not only enhance environmental stewardship but also position businesses as leaders in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
FAQs
What ESG data do cotton gins need to report first?
Cotton gins should focus on tracking and reporting essential metrics like land use, soil loss, water use, soil carbon levels, greenhouse gas emissions, and energy consumption. Collecting and sharing this data is crucial for aligning with industry standards and achieving sustainability objectives.
How can a gin prove cotton traceability to brands?
Gins can demonstrate cotton traceability by leveraging systems like blockchain, certifications, and chain-of-custody frameworks. Tools such as physical tracers (like DNA markers) and certifications, including the Better Cotton Initiative (BCI), Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), and the U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol, play a key role. These methods enable clear record-keeping from the farm to the gin, addressing brands’ expectations for responsible sourcing and transparency.
How do ESG improvements affect a gin’s costs and profits?
Enhancing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) efforts isn’t just good for the planet - it can also make a real difference to a gin company’s bottom line. For example, focusing on sustainable practices like conserving water, cutting energy use, or finding ways to repurpose waste can significantly cut operational costs while improving overall efficiency.
On top of that, ESG initiatives often resonate with eco-conscious consumers who are willing to pay a premium for products that align with their values. This means companies can justify higher prices, leading to better profit margins. Over time, these efforts also help reduce risks tied to stricter regulations or resource shortages, ensuring financial stability and keeping businesses aligned with both market demands and regulatory expectations.


